If you want the strongest 3d printer filament, look at PEEK and Polycarbonate. PEEK has a tensile strength between 67 and 83 MPa. Polycarbonate is known for being tough and lasting a long time. You check how strong a 3d printing material is by looking at tensile strength, impact resistance, chemical resistance, UV resistance, and temperature resistance. The table below shows how the strongest 3d printer filaments do in these areas:
|
Material |
Impact Resistance |
Chemical Resistance |
UV Resistance |
Temperature Resistance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Nylon |
High |
Excellent |
Moderate |
High |
|
Polycarbonate |
High |
Excellent |
Moderate |
High |
|
ABS |
Moderate |
Resistant |
Moderate |
Moderate |
|
PETG |
Moderate |
Better than PLA |
Good |
65°C - 75°C |
|
PLA |
Low |
Poor |
Low |
~55°C |
You can use this chart to help pick the strongest filament for your project.
Strength in 3D Printing Material
When you pick a 3d printing material, you should know what makes it strong. Material strength means how well it holds up to pulling and hitting. It also means how it handles chemicals, sunlight, and heat. These things help you choose the right filament for your project.
Here are the main things that show how strong a 3d printing material is:
|
Property |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Tensile Strength |
The most force a material can take before breaking |
|
Yield Strength |
The force where the material starts to change shape |
|
Young's Modulus |
How stiff and bendy the material is |
|
Elongation at Break |
How much it stretches before it snaps |
|
Toughness |
How much energy it takes before it breaks |
- Durability means the material can handle different weights and forces.
- Heat resistance means the filament will not melt when it gets hot.
Tensile Strength
Tensile strength tells you how much pulling a material can take before it snaps. If you want a strong filament, look for one with high tensile strength. Polycarbonate can take up to 66 MPa. Nylon can take between 50 and 90 MPa. TPU can take 50 MPa. These numbers help you see which filaments are strong and good for hard jobs.
|
Material |
Tensile Strength (MPa) |
|---|---|
|
Polycarbonate |
66 |
|
Nylon |
50-90 |
|
TPU |
50 |
Impact Resistance
Impact resistance shows how well a filament can take a hit or a drop. If you need strong parts that might get hit, check this property. Polycarbonate and nylon both do well here. TPU is also good. PLA+ is four times stronger than regular PLA.
|
Filament Type |
XY Impact Resistance (kJ/m2) |
Z Impact Resistance (kJ/m2) |
|---|---|---|
|
Polycarbonate (PC) |
Over 31.5 |
1.8 - 5.4 |
|
Nylon (PA) |
Does not break |
5.4 - 10.1 |
|
TPU |
200 MPa |
N/A |
|
PLA+ |
4 times stronger than PLA |
8.7 |
Chemical Resistance
Chemical resistance helps you pick a filament for places with oils or acids. Polycarbonate stands up to many chemicals like oils and alcohols. PEEK is good against both organic and inorganic stuff. Nylon can handle alkalis and weak acids. ABS works well with some acids and salts.
|
Filament |
Chemical resistance |
|---|---|
|
PC |
Stands up to oils, alcohols, greases, waxes |
|
PEEK |
Good against organic and inorganic things |
|
Nylon |
Handles alkalis, weak acids, oxidizers |
|
ABS |
Works with acids, chlorides, salts, solutions |
UV Resistance
UV resistance means the filament does not break down in sunlight. If you want strong parts for outside, pick a filament with high UV resistance. PETG is good for outdoor use and blocks UV rays. ASA is the best for UV resistance and does not fade or crack. ABS can block UV if you add special stuff.
- PETG: Blocks UV rays, good for outside.
- ASA: Best for UV, does not fade or crack.
- ABS: Needs special stuff to block UV.
Temperature Resistance
Temperature resistance tells you how much heat a material can take before it melts or gets weak. Polycarbonate is one of the best for high heat, up to about 290°C. Continuous fiber filaments can take up to 245°C. Conductive filaments work up to 220°C.
|
Filament Type |
Maximum Operating Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|
|
Polycarbonate (PC) |
290±20 |
|
Continuous Fiber |
245±15 |
|
Conductive Filament |
220±10 |
Tip: If you need a filament for hot places, pick polycarbonate or continuous fiber filament.
Strongest 3D Printer Filaments
If you want the strongest 3d printer filaments, you should see how they work in real life. You can look at things like tensile strength, impact resistance, and temperature resistance. The table below helps you compare the strongest filaments:
|
Filament |
Tensile Strength (PSI) |
Temperature Resistance (°C) |
Impact Resistance |
|---|---|---|---|
|
PEEK |
7250 |
>250 |
High |
|
Nylon |
7000 |
N/A |
High |
|
ABS |
4700 |
220-250 |
Good |
|
PLA |
7250 |
190-220 |
N/A |
|
PETG |
7000 |
220-260 |
N/A |
|
TPU |
4000 |
N/A |
Excellent |
|
Polycarbonate |
5200 |
Up to 140 |
Excellent |
PEEK
PEEK is one of the strongest 3d printer filaments you can use. It has high tensile strength and can take a lot of heat. PEEK also does not break easily when hit. It can handle heat over 250°C and stays strong under pressure. People use PEEK in cars, planes, and hospitals. It can replace metal because it is light and strong. PEEK does not get damaged by chemicals or wear. It is good for hard jobs. If you print with the right settings, your parts will be the right size.
Tip: Pick PEEK if you need strong and tough parts that face heat, chemicals, or heavy weight.
- Automotive: Safety parts and energy absorption
- Aerospace: Lightweight fixtures with high strength
- Medical: Dental tools and surgical devices
Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate is one of the strongest 3d printer filaments for taking hits. It is very tough and has good tensile strength. Polycarbonate keeps its shape even when it gets hot, up to 140°C. You can use it for safety gear, car parts, and test models. Polycarbonate is not as strong as PEEK, but it is still very tough and lasts a long time.
- Polycarbonate can take hits and keeps things safe.
- You can use it for strong parts in many projects.
Nylon
Nylon is a great choice if you want strong, flexible parts. It is light but still very strong. Nylon has high tensile strength and can take hits well. It does not get damaged by chemicals or wear. You can use nylon for gears, bushings, and moving parts. Nylon melts at a high temperature, so you can use it in more places than PLA or PETG.
|
Advantage |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Makes lightweight but strong parts |
|
|
Chemical resistance |
Handles chemicals and solvents |
|
Wear resistance |
Good for parts with friction |
|
Cost-effectiveness |
Saves money and time |
|
Excellent layer adhesion |
Keeps prints strong and accurate |
ABS
ABS is a strong 3d printer filament for everyday things. It has good tensile strength and can take hits. ABS can handle heat up to 100°C before it gets soft. You can use ABS for toys, covers, and car parts. ABS works better than PLA in heat, but it can change shape if it gets too hot for too long.
- ABS keeps its shape in some heat.
- You can use ABS for parts that need to be tough.
TPU
TPU is a bendy filament that is still very strong. It can take hits and does not wear out fast. TPU bends and stretches like rubber. You can use it for phone cases, gaskets, and things that need to absorb shocks. TPU does not tear or get scratched easily, so it is good for parts that need to bend and last.
Note: TPU is best for parts that need to bend, stretch, or take hits.
Carbon Fiber
Carbon fiber filament is very strong and stiff. It is light but can hold a lot of weight. Carbon fiber filaments do not change shape in heat and stay strong. You can use carbon fiber for drone frames, car parts, and tools. This filament does not warp or shrink much, so your prints stay the right size.
|
Property |
Description |
|---|---|
|
High Strength |
Strong and lightweight |
|
Dimensional Stability |
Keeps prints precise |
|
High Heat Deflection Temp |
Works in hot environments |
You can make strong and light parts with carbon fiber.
I-BEAM IMPACT PLA
I-BEAM IMPACT PLA is a new strong 3d printer filament. It is much tougher than regular PLA. This filament is easy to print and works well for test parts and real parts. I-BEAM IMPACT PLA keeps its strength and shape better than normal PLA. You can use it for parts that might get dropped or hit.
I-BEAM IMPACT PLA is a good choice if you want strong and easy-to-print filaments.
When you pick the strongest 3d printer filaments, make sure you choose the right one for your project. You get the best results when you use the best filament for your needs.
Use Cases
Functional Prototypes
You need strong materials for working prototypes. These parts should act like the final product. Polycarbonate is very tough and does not break easily. Nylon bends but stays strong, so it works for gears. PETG is good outside because it can handle hits and bad weather. If you test parts that hold weight, these filaments show how your design works under stress.
Tip: Pick strong filaments for prototypes that face real forces.
- Polycarbonate (PC): Very tough and does not break, good for working parts.
- Nylon (Polyamide): Stays strong and bends, great for gears and moving parts.
- PETG: Tough and handles hits, works well outside.
End-Use Parts
You want filaments that last and do not break for finished parts. ABS is strong and does not melt fast, so it works for car parts and tools. PETG is easy to print and does not get ruined by water, so it is good for things outside. TPU bends and stays strong, so it is best for phone cases and seals. These filaments keep their strength when holding weight, so your parts last longer.
- ABS: Strong and does not melt fast, good for tough parts.
- PETG: Does not get ruined by water and does not bend out of shape.
- TPU: Bends and lasts, best for seals and cases.
Outdoor Applications
Outdoor parts need to stand up to sun, rain, and heat. You need filaments that block UV rays and bad weather. ASA is best for blocking UV and weather. Polycarbonate has UV blockers and works in hot places. Nylon lasts a long time, but sun can make it weaker. PETG and TPU can handle weather, but ASA and polycarbonate are better for outside.
|
Filament Type |
UV Resistance |
Weather Resistance |
Durability |
Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
ASA |
High |
Yes |
High |
Best for outside, blocks UV rays very well. |
|
Polycarbonate |
Excellent |
Yes |
High |
Has UV blockers, works in hot places. |
|
Nylon |
Moderate |
Yes |
High |
Bends well, but sun can make it weaker. |
|
TPU |
Low |
Yes |
Moderate |
Bends and lasts, not for lots of sun. |
|
PETG |
Moderate |
Yes |
High |
Blocks some UV, not as good as ASA or polycarbonate. |
High-Temperature Environments
You need filaments that stay strong in high heat for tough jobs. Essentium PEKK works up to 280°C, so it is good for planes and cars. SABIC ULTEM 9085 does not burn and works up to 210°C. BASF PAHT CF15 has carbon fibers for extra strength and heat. Polymaker PC-Max does not break easily and works up to 140°C. These filaments help you print parts that hold weight and stay strong in hot places.
- Essentium PEKK: Handles heat up to 280°C, good for planes and cars.
- SABIC ULTEM 9085: Handles heat up to 210°C, does not burn.
- BASF PAHT CF15: Handles heat up to 150°C, has carbon fibers.
- Polymaker PC-Max: Handles heat up to 140°C, tough and costs less.
Chemical Exposure
Labs and factories need filaments that do not get ruined by chemicals. ULTEM 1010 is good because it does not melt and stands up to chemicals. Kynar PVDF and Solef PVDF AM Filament work well in places with strong chemicals. PVDF does not get ruined by many acids, bases, and other chemicals. You can use these filaments for parts that need to stay strong when they touch chemicals.
- ULTEM 1010: Does not melt and stands up to chemicals.
- Kynar PVDF: Made for places with strong chemicals.
- Solef PVDF AM Filament: Made to block chemicals.
- PVDF: Blocks acids, bases, and other strong chemicals.
Note: Use chemical-resistant filaments for parts in labs or factories.
Choosing the Right 3D Printer Filament
Application Needs
Think about what you want your part to do. Pick a filament that fits your needs. If you need something strong or flexible, choose the right type. PEEK works for jobs with lots of heat and stress. Nylon is good if you want parts that bend and last. PETG is easy to use and works well outside.
Here is a table to help you pick the best filament:
|
Criteria |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Filament Diameter |
Make sure the size matches your printer. |
|
Printer Capabilities |
Check if your printer can use the filament. |
|
Material Properties |
Look for strength, flexibility, and heat resistance. |
|
Application Needs |
Think about what your part will do and where it goes. |
Tip: Always think about how you will use your print. Learn about each filament before you pick one.
Printer Compatibility
Your printer must work with the filament you choose. Some printers only use certain filaments. Check the nozzle size and temperature range. PEEK needs very high heat from your printer. ABS and PETG are easier and work with most printers.
- Nozzle size changes how much detail you get. Most printers use 0.4 mm nozzles. Some filaments need bigger or smaller nozzles.
- Printing temperature is different for each filament. PLA prints at low heat. PEEK needs up to 300°C.
- Some filaments need special printers. PEEK needs advanced printers. ABS works with basic printers.
- Even if you pick a strong filament, printer settings and design matter most for strength.
Cost vs. Performance
You want good results without spending too much. Filaments like PEEK and carbon fiber cost more but are stronger. PETG and ABS are cheaper and work for many jobs. Think about your budget and what your part needs to do.
- Project needs: Pick a filament that fits your job.
- Printer compatibility: Make sure your printer can use the filament.
- Cost vs. performance: Balance price and features.
- Easy to use: If you are new, try PETG first.
- After printing: Some filaments need extra steps to look or work better.
- Too much infill uses more filament and time. Use just enough infill.
- Strong infill patterns help your part last longer.
- Thick walls make your print stronger.
- Add more infill at stress points to stop breaks.
- Always match the filament to your project for the best results.
You should pick a filament that matches your project. Think about strength, flexibility, and heat resistance. Polycarbonate, nylon, and TPU are strong choices. They have high tensile strength, as you can see here:
|
Filament Type |
Approx Tensile Strength |
|---|---|
|
Polycarbonate (PC) |
70 MPa |
|
Nylon (PA) |
50–80 MPa |
|
TPU |
20–50 MPa |
If the air is dry, prints turn out stiffer and better. Keep filaments in closed containers to protect them.
Check your printer’s heat range and nozzle size before you start. PETG and ABS are good for beginners. For outdoor or tough jobs, use nylon carbon fiber or PP GF30.
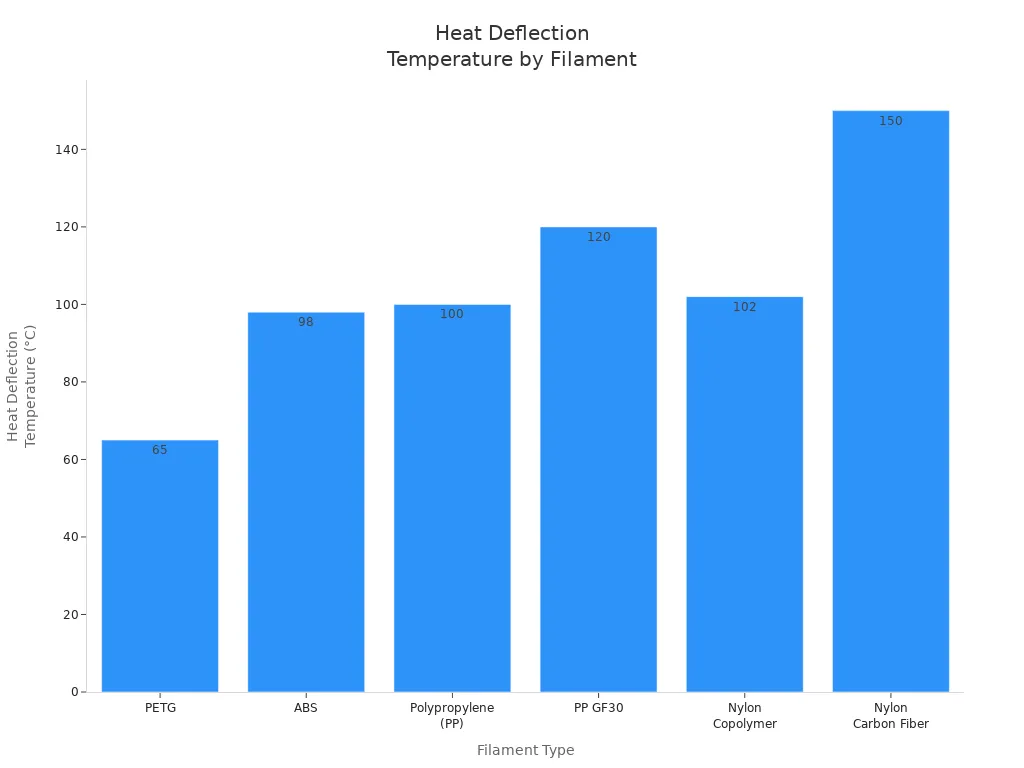
Pick the strongest filament that works with your printer and project. This helps you get the best results.
FAQ
What is the strongest 3D printer filament I can use at home?
You can use polycarbonate or nylon for strong prints at home. These filaments fit most desktop printers. PEEK is even stronger, but you need a special printer that gets very hot.
Can I print strong parts with a regular 3D printer?
You can make strong parts with ABS, PETG, or nylon. Use more infill and thicker walls to make prints tougher. Make sure your printer gets hot enough for your filament.
How do I store strong filaments like nylon or PEEK?
- Keep filaments dry.
- Put them in airtight containers or vacuum bags.
- Add silica gel packs to soak up water.
Water can make your prints weak and not work well.
Which filament is best for outdoor use?
|
Filament |
UV Resistance |
Weather Resistance |
|---|---|---|
|
ASA |
Excellent |
Excellent |
|
PETG |
Good |
Good |
|
Polycarbonate |
Good |
Good |
ASA is the best for outdoor parts. PETG and polycarbonate also work well outside.









