A high-precision 3D printer produces objects with fine detail, accurate dimensions, and smooth surfaces. Print quality and resolution determine the level of detail a printer can achieve. Material compatibility expands the range of possible projects. Ease of use and simple maintenance help users achieve consistent results. Many industries rely on precise 3D printing for specialized applications.
|
Industry |
Applications |
|---|---|
|
Healthcare |
Customized dental implants, prosthetic limbs, surgical planning models, drug delivery devices |
|
Aerospace |
Lightweight components, cabin fixtures, engine parts, satellites for space missions |
|
Automotive |
Conceptual designs, manufacturing replacement parts, rapid prototyping |
|
Consumer Goods |
Custom-fitted products, personalized designs, fashion items like shoes |
|
Fashion |
Unique jewelry, custom decor, tailored footwear |
Users should define their specific needs before choosing a printer.
Key Takeaways
- Identify your specific needs before choosing a 3D printer. Consider the size and detail of the objects you want to create.
- Understand the importance of print quality and resolution. Higher resolution means better detail but may increase print time.
- Evaluate the materials your printer can use. Different materials affect the strength and appearance of your prints.
- Consider the ease of use and maintenance of the printer. User-friendly features can save time and reduce errors.
- Research brands and read user reviews. A reputable brand often means better support and fewer issues.
What Is a High-Precision 3D Printer
A high-precision 3D printer stands out by delivering detailed, accurate, and smooth prints. These machines use advanced technology to achieve fine resolution and tight tolerances. Precision depends on several factors, including resolution, accuracy, and tolerance. Technology, materials, and environmental conditions also play important roles.
Print Quality and Resolution
Print quality refers to how well a printer can reproduce fine details. Resolution measures the smallest movement or feature a printer can create. Most high-precision 3D printers offer resolutions between 2 microns and 50 microns. The table below shows typical technical specifications:
|
Specification |
Value |
|---|---|
|
Resolution |
2µm ~ 50µm |
|
Tolerance |
+/- 10µm ~ 25µm |
Many printers achieve a layer height of about 50 microns. Some, like those from Ultimaker, provide a range from 20 to 60 microns, depending on the nozzle size. However, high resolution alone does not guarantee accuracy.
Layer Height and Feature Size
Layer height affects both the smoothness and detail of a printed object. FDM printers usually reach a minimum layer height of 0.05 mm, while SLA and DLP printers can go as low as 0.025 mm. Lower layer heights increase print time but improve detail. The smallest feature size that a high-precision 3D printer can reliably produce is about 0.1 mm (0.004 in).
|
Feature Size |
Measurement |
|---|---|
|
Minimum Detail Size |
0.1 mm (0.004 in) |
Accuracy and Surface Finish
Accuracy describes how closely the printed object matches the original design. Tolerances vary by technology, as shown in the chart below:
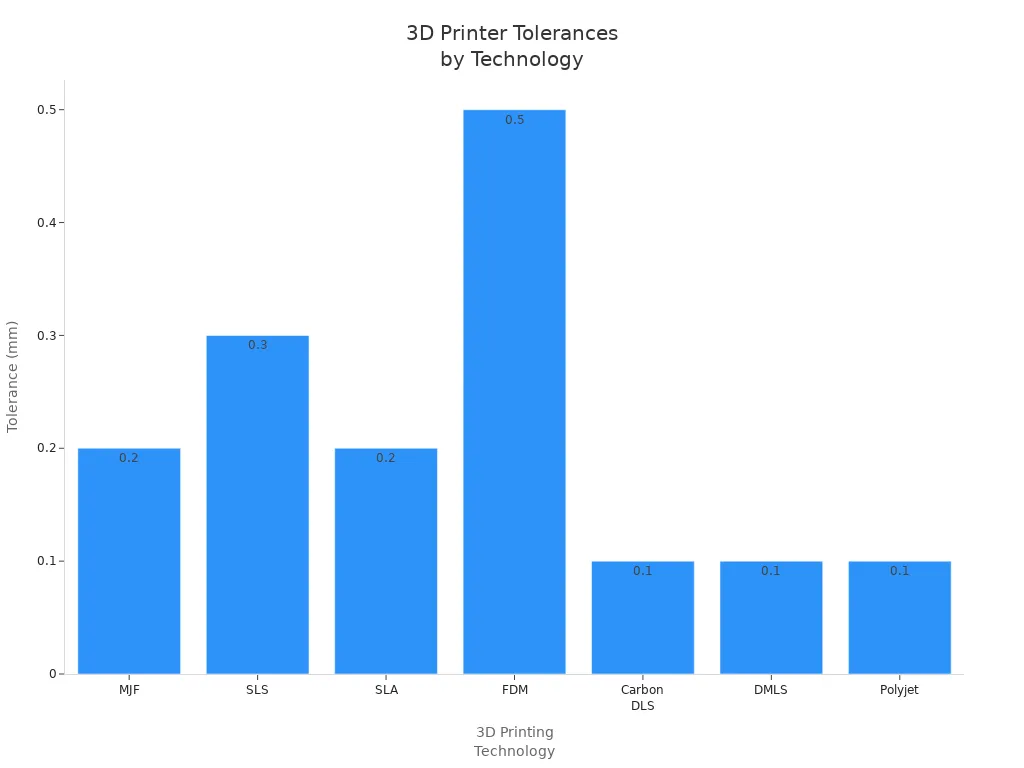
Surface finish also differs by technology. SLA printers produce smooth surfaces with minimal visible layers, making them ideal for detailed work. FDM printers often show visible layer lines and may need extra finishing. SLS printers offer a balance, with smooth but slightly granular surfaces.
|
Technology |
Surface Finish Quality |
Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
|
FDM |
Limited surface quality, visible layer lines |
Typical layer heights of 50-400 microns, requires post-processing |
|
SLA |
Superior surface finish, minimal visible layer lines |
Layer heights as fine as 25-100 microns, smooth surfaces, high detail |
|
SLS |
Smooth but more granular than SLA |
Uses powdered thermoplastics, no support structures needed, robust parts |
A high-precision 3D printer combines fine resolution, tight tolerances, and excellent surface finish to meet demanding project requirements.
Assessing Your Needs
Application and Object Size
Every project starts with a clear goal. Users should identify what they want to create and how large each object will be. Some projects require small, detailed parts, while others need larger models. For example, dental models and jewelry pieces demand compact sizes with intricate features. In contrast, engineering prototypes or architectural models often involve bigger dimensions. The table below shows how different factors influence the choice of a high-precision 3D printer:
|
Factor |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Resolution |
Determines the level of detail achievable, often measured by layer height or minimum feature size. |
|
Calibration |
Involves fine-tuning parameters to ensure accurate material deposition for precise prints. |
|
Mechanical Stability |
A sturdy printer frame reduces vibrations, leading to more precise prints. |
|
Material Properties |
Affects part output precision due to factors like shrinkage rates and thermal properties. |
|
Design Considerations |
Intricate designs may require specific techniques to maintain accuracy during printing. |
|
Post-processing |
Additional steps after printing can impact the final part's accuracy. |
Required Detail Level
The level of detail needed depends on the application. Jewelry designers look for highly polished surfaces and sharp textures. Medical and dental professionals need detailed models for surgical planning and custom devices. DLP and SLA printers often serve these industries because they deliver excellent precision. When choosing a printer, users should consider:
- Layer height: Finer layers create smoother surfaces but increase print time.
- Nozzle diameter: Smaller nozzles improve detail but slow down production.
- Print speed: Slower speeds enhance detail but extend the time needed for each print.
Tip: Higher precision usually means longer print times and higher costs. Users should balance detail with efficiency.
Production Volume
Production volume affects the best manufacturing method. For low to mid-volume runs, a high-precision 3D printer offers flexibility and supports complex designs. When producing more than 500 parts, the cost per unit rises with 3D printing. Injection molding becomes more cost-effective for high-volume production. The table below compares both methods:
|
Factor |
3D Printing |
Injection Molding |
|---|---|---|
|
Per-Unit Cost |
High for large volumes |
Low |
|
Part Production Speed |
Moderate |
Fast |
|
Best for |
Low-to-mid volumes, complex parts |
High-volume standardized parts |
Users should match their printer choice to their project size, detail needs, and expected production volume.
Key Features to Compare
Supported Materials
Material compatibility plays a major role in the versatility of any high-precision 3D printer. Each material brings unique properties that affect the final print's strength, durability, and appearance. The table below highlights some of the most commonly supported materials and their impact on print quality:
|
Material |
Characteristics |
Impact on Print Quality |
|---|---|---|
|
PLA |
Biodegradable, easy to use, low cost |
Ideal for beginners, minimal warping |
|
PETG |
Durable, chemical resistant |
Better durability than PLA |
|
ABS |
Strong, heat resistant |
Suitable for functional parts |
|
PA12 |
High strength, durable, chemical resistant |
Used for strong prototypes and production parts |
|
PEEK |
Exceptional strength, heat resistance |
High-performance applications |
Material compatibility affects more than just the look of a part. It influences mechanical performance, thermal stability, and how the material behaves during printing. Users must consider factors like moisture sensitivity, warping, and interlayer adhesion. These details help ensure the chosen printer matches the functional requirements of each project.
Print Speed and Reliability
Print speed and reliability determine how efficiently a printer can produce high-quality parts. Faster print speeds can save time, but they may reduce detail or increase the risk of errors. Reliability ensures that the printer consistently delivers accurate results, even during long or complex jobs.
Manufacturers use several metrics to measure reliability and accuracy. The table below explains some of these important metrics:
|
Metric |
Description |
Application |
|---|---|---|
|
Hausdorff Distance |
Maximum surface deviation |
Precision-critical tasks (e.g., CAD) |
|
RMSE |
Overall accuracy |
General accuracy checks |
|
MAE |
Point-by-point accuracy |
Sparse or detailed datasets |
|
Surface Coverage |
Completeness |
Missing features detection |
|
Reconstruction Accuracy |
Shape fidelity |
Complex geometries |
|
Mesh Quality |
Topology assessment |
3D printing and rendering |
|
Texture Resolution |
Visual detail & performance |
Game assets and architectural renders |
A reliable high-precision 3D printer maintains consistent performance across different projects. Users should look for models that balance speed with accuracy and minimize print failures.
Ease of Use and Maintenance
Ease of use and maintenance can make or break the 3D printing experience. Some printers require frequent calibration or manual adjustments, while others offer automated features that simplify operation. Maintenance needs vary significantly among different printer models and technologies. Predictive maintenance strategies can help users schedule service and reduce downtime. Maintenance costs also differ based on the printer's design and technology.
Tip: Choosing a printer with user-friendly controls and clear maintenance guidelines can save time and prevent costly mistakes.
Software Compatibility
Software compatibility shapes the entire 3D printing workflow. The right software can streamline file preparation, optimize print settings, and monitor progress remotely. Popular platforms include Netfabb, 3DPrinterOS, and Markforged Eiger. The table below compares their key features:
|
Software Platform |
Key Features |
Primary Use Case |
Pros |
Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Netfabb |
Comprehensive tools for analysis and repair, automatic/manual repair, file conversion, model optimization |
Preparing STL files for printing |
Precision in model issue detection, enhances print reliability |
N/A |
|
3DPrinterOS |
Cloud-based, remote print monitoring, integrated slicer, file management |
Managing 3D printing operations across multiple devices |
Centralized platform, accessible from any device |
Reliance on internet connectivity, subscription-based pricing |
|
Markforged Eiger |
Cloud-based, advanced slicing for Markforged materials, build queue management |
Preparing and managing prints on Markforged printers |
Seamless integration with Markforged hardware |
Exclusively for Markforged printers, subscription required |
Effective management of slicing software can optimize infill patterns and support structures. This reduces material waste and improves the strength and quality of printed parts. The choice of CAD software and slicing methods also influences the accuracy of the final product. Software compatibility directly impacts workflow efficiency and the overall success of high-precision 3D printing projects.
Choosing the Right High-Precision 3D Printer
Selecting the best high-precision 3D printer involves careful research and comparison. Users should match printer technology, build volume, and budget to their specific needs. Each factor plays a key role in the final decision.
Technology Types (FDM, SLA, SLS)
Different 3D printing technologies offer unique strengths. Users should compare these options to find the best fit for their projects.
|
Technology |
Print Quality |
Precision |
Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
|
FDM |
Moderate, visible layer lines |
Limited fine detail resolution |
Fast turnaround, low-cost prototyping, suitable for larger parts |
|
SLA |
High, smooth surface finish |
High precision, ideal for fine details |
Cures resin with UV laser, suitable for visual models and fit assessments |
|
SLS |
Moderate, naturally coarse finish |
Good for complex geometries |
Fuses powdered nylon, durable parts, no support structures needed |
FDM printers work well for quick prototypes and larger objects. SLA printers deliver smooth surfaces and fine details, making them ideal for jewelry, dental models, and visual prototypes. SLS printers handle complex shapes and produce strong, functional parts. Some advanced systems, such as Direct Metal Laser Sintering and Desktop Metal Studio, print with metals and super alloys. These machines create durable end-use parts for demanding industries.
Tip: Users should research each technology and consider the types of materials, part sizes, and detail levels required for their projects.
Build Volume
Build volume determines the maximum size of objects a printer can produce. A larger build volume allows users to print bigger items in one piece. This feature is essential for projects like automotive parts or furniture components. Batch printing becomes possible with a larger build area, letting users create multiple items at once and save time.
- Larger build volumes support the creation of big objects in a single print.
- Batch printing increases efficiency by producing several parts together.
- Standard desktop printers often have a limited build volume, which may not suit large projects.
Users should evaluate their typical project sizes before choosing a printer. A high-precision 3D printer with a suitable build volume ensures flexibility for both small and large tasks.
Budget Considerations
Cost plays a major role in selecting a high-precision 3D printer. Prices vary widely based on features, technology, and intended use.
|
Category |
|
|---|---|
|
Low-end |
$4,000 - $20,000 |
|
Mid-range |
$20,000 - $100,000 |
|
Industrial-level |
+$100,000 |
Operating costs also differ by printer type. FFF printers offer a low-cost entry point for industrial printing and work well for prototyping. SLA printers cost more but provide excellent resolution and surface finish. SLS and MJF printers have higher operating costs but deliver strong, functional parts for demanding applications.
|
Printer Type |
Description |
|
|---|---|---|
|
FFF |
Low |
Accessible entry point for industrial printing, suitable for prototyping and short-run production. |
|
SLA |
Mid |
Exceptional resolution and surface finish, ideal for detailed parts. |
|
SLS |
High |
Strong, functional nylon components for demanding applications. |
|
MJF |
High |
Combines speed, precision, and consistent part quality for production environments. |
A careful review of technology, build volume, and budget helps users select the right high-precision 3D printer for their goals. Matching these features to project requirements leads to better results and long-term satisfaction.
Model Comparison and Evaluation
Brand Reputation
Brand reputation plays a key role when choosing a high-precision 3D printer. Well-known brands often deliver consistent quality and reliable performance. Companies with strong reputations usually invest in research and development. They also provide better customer support and regular software updates. Some leading brands in the 3D printing industry include:
- Ultimaker: Known for user-friendly interfaces and reliable hardware.
- Formlabs: Recognized for high-resolution SLA printers.
- Markforged: Specializes in industrial-grade composite and metal printers.
- Stratasys: Offers a wide range of professional and industrial solutions.
User Reviews
User reviews give real-world insights into a printer’s strengths and weaknesses. Buyers should read reviews on trusted platforms, such as manufacturer websites, independent tech blogs, and online forums. Reviews often highlight:
- Print quality and consistency
- Ease of setup and daily use
- Customer service experiences
- Common technical problems
A table can help organize key points from user feedback:
|
Aspect |
Positive Feedback |
Negative Feedback |
|---|---|---|
|
Print Quality |
High detail, smooth finish |
Occasional misprints |
|
Reliability |
Consistent performance |
Rare hardware failures |
|
Support |
Helpful, responsive |
Slow response times |
User experiences can reveal issues not found in technical specs. They also help buyers set realistic expectations.
Warranty and Support
Warranty and support protect the investment in a high-precision 3D printer. Most reputable brands offer at least a one-year warranty. Some provide extended coverage for an extra fee. Good support includes:
- Quick response to technical questions
- Access to replacement parts
- Clear maintenance instructions
Comparing models by brand reputation, user reviews, and support options helps buyers make informed decisions. This approach leads to greater satisfaction and better results in high-precision 3D printing.
Practical Buying Steps
Requesting Sample Prints
Many manufacturers and resellers offer sample prints to show what their 3D printers can achieve. These samples help buyers judge the printer’s real capabilities. A sample print lets users check surface finish, detail, and accuracy. They can also compare different models side by side.
Steps to request and evaluate sample prints:
- Contact the manufacturer or authorized reseller.
- Ask for a sample that matches your typical project.
- Inspect the sample for fine details, smoothness, and strength.
- Compare samples from several brands.
Evaluating Real-World Performance
A printer’s technical specs do not always match real-world results. Testing the printer with your own files gives a better idea of its performance. Many sellers allow on-site demonstrations or remote print tests.
Key factors to check during evaluation:
- Print consistency over several jobs
- Ease of setup and calibration
- Noise level during operation
- Time required for maintenance
A table can help organize your findings:
|
Factor |
Model A |
Model B |
Model C |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Print Quality |
|
|
|
|
Reliability |
|
|
|
|
Ease of Use |
|
|
|
|
Maintenance Time |
|
|
|
Future-Proofing
Technology changes quickly. Buyers should choose a printer that can adapt to new needs. Look for models with upgradable hardware or software. Check if the manufacturer offers regular updates and strong support.
Consider these points for future-proofing:
- Modular components for easy upgrades
- Open material compatibility
- Active user community and support channels
Choosing a high-precision 3D printer requires careful attention to print quality, supported materials, and ease of use. Readers should focus on features that match their project needs and budget. Next steps include making a shortlist, requesting sample prints, and arranging demos.
Ongoing support and regular maintenance help users achieve the best results and extend printer life.
FAQ
What is the difference between resolution and accuracy in 3D printing?
Resolution describes the smallest detail a printer can produce. Accuracy measures how closely the printed object matches the original design. High resolution does not always guarantee high accuracy.
How often should users perform maintenance on a high-precision 3D printer?
Most manufacturers recommend basic maintenance after every 10–20 prints. Users should clean nozzles, check belts, and inspect moving parts regularly. Always follow the maintenance schedule in the user manual.
Can high-precision 3D printers use multiple materials?
Some high-precision printers support multiple materials. Users should check the printer’s specifications. A table in the manual often lists compatible materials, such as PLA, ABS, or resin.
|
Printer Model |
Supported Materials |
|---|---|
|
Model A |
PLA, ABS |
|
Model B |
Resin, PETG |
Do high-precision 3D printers require special software?
Most high-precision printers need slicing software to prepare files. Some brands include proprietary software. Others work with popular third-party programs. Users should verify software compatibility before purchasing.
What are common issues with high-precision 3D printers?
Print failures, clogged nozzles, and calibration errors often occur. Users can prevent most problems with regular maintenance and careful setup.









