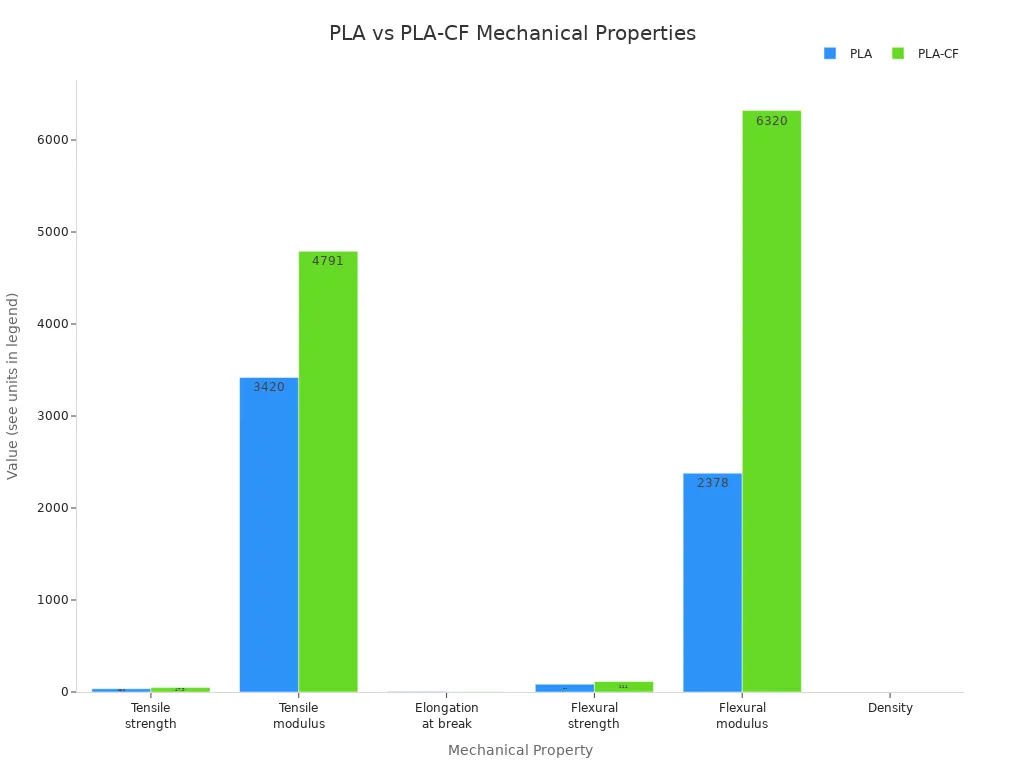
PLA-CF filament combines polylactic acid with chopped carbon fiber, creating a material designed for high-performance 3D printing. This cf blend increases strength, stiffness, and durability compared to standard PLA filament. The table below shows how PLA-CF outperforms PLA in key mechanical properties:
|
Property |
PLA |
PLA-CF |
|---|---|---|
|
Tensile strength (MPa) |
35.6 |
47.9 |
|
Tensile modulus (MPa) |
3420 |
4791 |
|
Elongation at break (%) |
4.2 |
2.0 |
|
Flexural strength (MPa) |
85.2 |
114 |
|
Flexural Modulus (MPa) |
2378 |
6320 |
|
Density (g/m3) |
1.24 |
1.29 |
Users choose PLA CF filament for projects that need lightweight, rigid parts. The cf content gives a matte finish and resists wear, making this filament ideal for functional prototypes and engineering applications.
Key Takeaways
- PLA-CF filament combines polylactic acid with carbon fiber, resulting in stronger and stiffer 3D prints compared to standard PLA.
- This filament is ideal for functional prototypes and engineering parts due to its lightweight nature and enhanced durability.
- Users should use hardened steel nozzles for printing PLA-CF to prevent clogs and ensure smooth extrusion.
What Is PLA-CF?
PLA Carbon Fiber Filament Composition
PLA-CF stands for carbon fiber reinforced PLA. Manufacturers create this filament by blending polylactic acid with chopped carbon fiber. The result is a material that combines the printability of PLA with the strength and rigidity of carbon fiber. Most brands use a ratio of 5% to 10% carbon fiber in the mix. This balance allows the filament to maintain good flow through the printer nozzle while boosting mechanical performance.
|
Carbon Fiber Ratio (%) |
|
|---|---|
|
100 |
0 |
|
95 |
5 |
|
90 |
10 |
The carbon fiber reinforcement increases the high strength-to-weight ratio of the filament. This makes PLA carbon fiber filament a popular choice for engineers and hobbyists who need lightweight but strong parts. The cf particles also give the finished print a unique matte texture and improved wear resistance.
Note: The addition of cf not only improves mechanical properties but also enhances thermal conductivity. PLA-CF filament can reach a thermal conductivity of 37.1 W/mK at a 9.5% carbon fiber volume fraction. This value is much higher than standard PLA, although actual results may vary due to fiber breakage during printing.
PLA-CF vs PLA
PLA-CF offers several advantages over regular PLA. The carbon fiber reinforcement changes the way the filament behaves during and after printing. PLA carbon fiber filament is stiffer and more durable than standard PLA. It also resists deformation and shrinkage, which helps maintain dimensional accuracy in printed parts.
|
PLA |
PLA-CF |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Tensile Strength (MPa) |
54.51 |
49.41 |
|
Young's Modulus (GPa) |
1.04 |
1.26 |
|
Elongation-at-Break (%) |
6.26 |
7.81 |
PLA-CF filament costs more than regular PLA. The table below shows the difference in price and properties:
|
Filament Type |
Properties |
|
|---|---|---|
|
PLA |
Generally lower cost |
Easy to print |
|
PLA-CF |
Generally higher cost |
Strong, ductile, wear resistant, heat tolerant |
PLA carbon fiber filament also has a different environmental impact. The production process for PLA-CF is more complex because it combines two materials. Recycling is more difficult, and the carbon fiber content can slow down degradation. The table below compares the environmental aspects of PLA-CF and PLA:
|
Aspect |
PLA-CF Production |
Standard PLA Production |
|---|---|---|
|
Mechanical Properties |
Enhanced due to carbon fiber reinforcement |
Standard mechanical properties |
|
Recycling Considerations |
More complex due to composite nature |
Easier, but still requires careful management |
|
Environmental Impact |
Potentially higher due to carbon fiber |
Slower degradation, potential ecosystem harm |
|
Resource Efficiency |
Mechanical recycling is resource-efficient |
Recycling is crucial to limit resource use |
PLA-CF filament stands out for its cf content, which provides extra rigidity and durability. Users often select PLA carbon fiber filament for functional prototypes and engineering parts that require precise dimensions and strength. The cf blend also improves heat tolerance, making it suitable for applications where standard PLA might fail.
PLA-CF Properties & Durability
Strength and Stiffness
PLA carbon fiber filament stands out for its impressive mechanical properties. The addition of cf increases stiffness and strength, making printed parts more rigid than those made with standard pla. Flexural strength tests show that carbon fiber reinforcement boosts the mechanical properties of pla-cf. The effectiveness of cf depends on fiber orientation and layer adhesion during printing. When carbon fibers align with the load direction, stiffness improves. Lack of orientation in the Z direction may weaken the material. Engineers value the mechanical properties of pla-cf for functional prototypes and structural components. The filament resists deformation and shrinkage, which helps maintain dimensional accuracy. These properties make pla carbon fiber filament a top choice for projects that demand high durability.
The mechanical properties of pla-cf include:
- Increased stiffness compared to pla
- Enhanced strength for load-bearing applications
- Reduced shrinkage during cooling
- Reliable dimensional stability
Printability and Matte Finish
Printability is a key advantage of pla carbon fiber filament. Users find that the filament flows smoothly through most 3D printers. The cf content improves printability by reducing warping and minimizing layer separation. However, the abrasive nature of cf can cause clogged nozzles and extrusion inconsistencies. Printers may need hardened steel nozzles to handle the filament. Severe ringing artifacts sometimes appear every 5mm on prints. Nozzle wear is common due to the mechanical properties of cf.
|
Parameter |
Temperature Range (°C) |
|---|---|
|
Nozzle temperature |
200–220 |
|
Bed temperature |
40–60 |
The matte finish of pla carbon fiber filament sets it apart from standard pla. The filament features a frosted texture because of the chopped cf, which enhances its matte appearance. Standard matte pla uses mineral nucleators to achieve a premium finish that hides layer lines and improves visual aesthetics. The shine-free surface of pla-cf appeals to designers who want a professional look. Printability and surface quality combine to make pla-cf ideal for engineering and display models.
Printability highlights:
- Smooth extrusion with proper nozzle selection
- Reduced warping and layer separation
- Matte finish that minimizes gloss and hides layer lines
- Frosted texture for enhanced visual appeal
Durability and Wear Resistance
Durability defines the value of pla carbon fiber filament. The cf reinforcement increases wear resistance, making printed parts last longer under stress. The mechanical properties of pla-cf help parts withstand repeated use and mechanical loads. Shelf life depends on storage conditions. Unopened filament lasts 1–2 years, while opened filament lasts 3–6 months. Properly stored filament can last up to 15 years or more.
|
Filament State |
Average Shelf Life |
Factors Influencing |
|---|---|---|
|
Unopened |
1–2 years |
Original packaging, low humidity |
|
Opened |
3–6 months |
Exposure to air, storage method |
|
Properly Stored |
1–15+ years |
Desiccants, airtight containers |
The durability of pla carbon fiber filament makes it suitable for functional prototypes, engineering parts, and lightweight components. The mechanical properties ensure that parts resist wear and maintain their shape over time. Users should watch for printer compatibility issues, such as clogged nozzles and nozzle wear. These problems can affect printability and durability. Choosing the right printer and storage method helps maximize the mechanical properties and shelf life of pla-cf.
Tip: Store pla carbon fiber filament in airtight containers with desiccants to extend shelf life and preserve mechanical properties.
The combination of mechanical properties, printability, and durability makes pla-cf a reliable choice for demanding 3D printing projects. The filament offers enhanced strength, stiffness, and wear resistance, setting it apart from standard pla and other materials.
PLA CF filament Applications & Tips
Best Uses for PLA-CF
Engineers and designers often choose PLA CF filament for projects that demand high-performance parts. This filament works well for functional prototypes, especially when the design requires lightweight yet strong components. Many users select PLA CF filament for structural parts, brackets, and drone frames. These applications benefit from the material’s dimensional stability and resistance to deformation. In comparison to standard pla, PLA CF filament offers better durability and stiffness. Makers also use this filament for automotive parts, robotics, and jigs where a lightweight yet strong build is essential. The unique properties of PLA CF filament make it a top choice for functional prototypes and end-use parts that need to maintain shape under stress.
Printing Tips for PLA-CF
Successful printing with PLA CF filament depends on the right printing settings and hardware. Users should adjust printing temperature and speed to match the filament’s requirements. Most printers work best with a nozzle temperature between 200°C and 220°C. Bed temperature settings usually range from 40°C to 60°C. In comparison to pla, PLA CF filament needs more attention to printing settings because of its abrasive nature.
For best results, use abrasion-resistant nozzles:
- Stainless steel nozzles last longer than brass nozzles.
- Hardened nozzles and extruder gears prevent wear from carbon fiber.
- Abrasion-resistant nozzles are designed for carbon fiber materials.
Users should check their printer’s compatibility before printing with PLA CF filament. Proper printing settings help avoid clogs and ensure smooth extrusion. In comparison to other materials, PLA CF filament may require slower printing speeds and higher retraction settings. These adjustments help achieve a clean finish and maintain the filament’s lightweight yet strong qualities. Careful attention to printing settings ensures that pla cf good for demanding, high-performance parts.
PLA-CF filament offers high strength, stiffness, and a matte finish, making it ideal for demanding prints. Users should assess their printer’s compatibility with pla and review common challenges:
- Print quality issues, such as missing sections or poor adhesion
- Filament clogs due to rigidity
- Machine compatibility concerns
|
Limitation |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Brittleness |
PLA-CF snaps under impact instead of bending |
|
Poor Toughness |
Lacks impact resistance |
|
Limited Heat Resistance |
Slightly higher than pla, but less than Nylon |
|
Abrasiveness |
Wears down parts and surfaces |
For further learning, resources like the ultimate 3D printing guide for pla cf filament provide detailed tips and benefits. Users should try pla for prototypes, engineering parts, and lightweight components.
FAQ
What makes PLA carbon fiber filament different from regular PLA?
PLA carbon fiber filament contains chopped carbon fibers. This addition increases strength and stiffness. PLA alone offers less durability and a smoother finish.
Can standard 3D printers use PLA carbon fiber filament?
Most desktop printers can print PLA carbon fiber filament. They need hardened steel nozzles. PLA filament does not require special hardware for printing.
Is PLA carbon fiber filament suitable for outdoor use?
PLA carbon fiber filament resists wear and deformation. PLA may degrade faster outdoors. Users should check environmental conditions before choosing filament for outdoor projects.